Whether you are planning new home construction or a major renovation to your existing home, heating and cooling occupies a significant part of the process. According to a National Association of Home Builders study, the heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) system makes up between four and five percent of new home construction expenses. Operational costs include about half of the total energy bill, plus regular system repairs and maintenance. When the system finally wears out in 15 to 20 years, expect to pay at least $15,000 to replace it.
Energy-efficient heating and cooling systems, such as geothermal and solar, are known for higher upfront costs, significantly lower operating costs, and a longer lifespan. We will compare geothermal vs. solar heating and cooling systems. Both offer unique capabilities to keep the home comfortable while reducing monthly bills. They also have a softer impact on the environment. Which is the better pick? Read on to learn more.
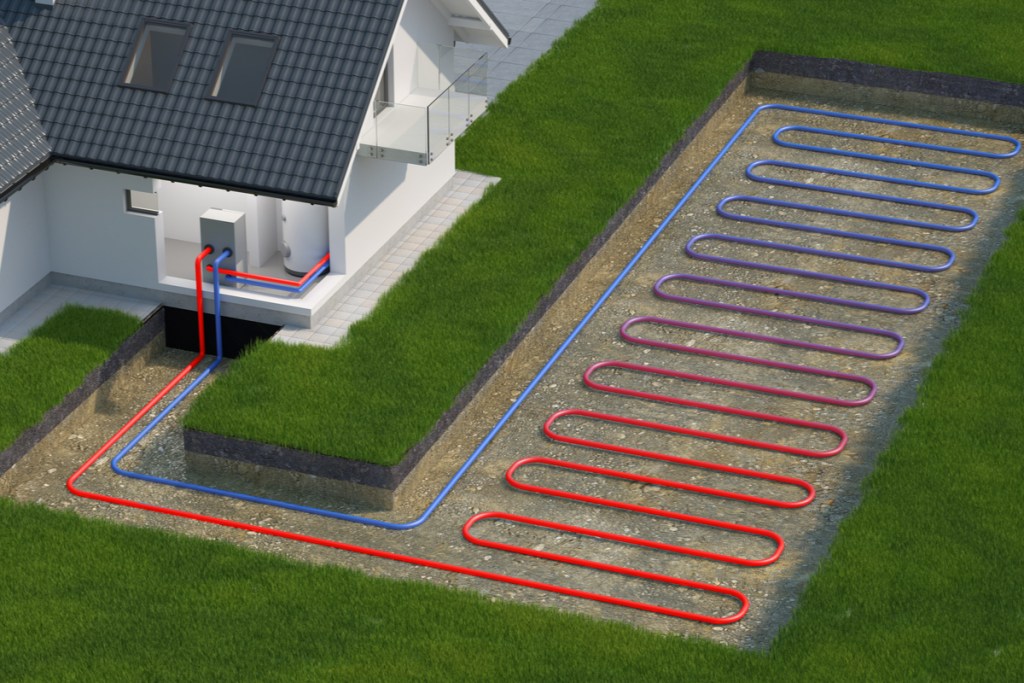
Geothermal
Outdoor air temperatures fluctuate significantly, but the soil temperature just a few feet below the surface remains relatively constant year-round. A geothermal system uses this “free energy” to heat and cool the home at five times the efficiency of standard systems.
How it works
Geothermal systems are known as heat pumps because they transfer heat between the home and the ground or a nearby water source. A pump moves fluid through looped tubes in the soil (or water) and back to the house. It compresses the passively heated fluid to increase the heating effect and discharges the heat inside the home. For cooling, simply switch the system into reverse mode.
There are four basic types of geothermal ground loop systems: Closed-loop horizontal, closed-loop vertical, closed-loop lake or pond, and open-loop groundwater. Closed-loop systems circulate a type of antifreeze that gains or dissipates heat in the soil, while open-loop systems intake water from a well or pond then discharge it into a pond or secondary well).
All of these loop types are suitable for both residential and commercial construction. Whether geothermal is a good fit and which system is best for an individual home will depend on climate, lot size, subsoil condition, and local installation costs. Water source or ground source heat pumps are useful in more extreme environments than air-source types.
System setup
The system includes the main geothermal heat pump unit, underground piping, and indoor ductwork. From a consumer standpoint, the biggest difference between geothermal and conventional HVAC lies in the fact that the burner is replaced with essentially a huge underground radiator coil. In a remodel scenario, the existing ductwork from a conventional system will likely work with a new geothermal setup.
The ideal loop configuration depends on the local conditions and budget. Horizontal loops are highly cost-effective to install but require an adequate lot size. Vertical loops may be a better choice for homes on smaller lots. Those with waterfront properties may consider closed-loop pond systems, which eliminate most of the system excavation costs by taking advantage of the thermal properties of deep water. Open-loop systems require a plentiful water source and sink (discharge site) for single-use water circulation.
Cost
Given a 2,500 square foot home, with heating and cooling requirements of 60,000 BTUs, a new geothermal HVAC system averages $20,000 to $30,000, installed. Users commonly see 30 to 60 percent savings on their monthly energy bills after switching from a conventional system. Expect the new heat pump to last about 20 to 25 years, with a replacement cost of about $7,000, while the underground piping lasts up to 50 years.
Environmental considerations
Whether you measure in dollars, greenhouse emissions, or carbon footprint, geothermal is better for the environment. It uses 25 to 50 percent less electricity than conventional HVAC, according to the EPA. It can reduce energy consumption by 44 percent compared with air-source heat pumps and 72 percent compared with standard HVAC equipment. And it burns no fossil fuel to generate heat.

Solar
In the current stage of solar heating and cooling, we need to separate the two functions. Active solar heating has its primary focus on capturing the sun’s heat energy directly for transfer into the home’s system. Conversely, in solar cooling, the sun’s energy is transformed into electricity to operate a heat pump cooling system. Since the best solar cooling systems are not currently capable of operating at night without power from the grid, we’ll focus on the available innovations in active solar heating.
How it works
In active solar thermal heating, the sun shines on the heat-transfer medium (liquid or air) inside a solar collector. Plate collectors are typically installed on the roof or the ground in a sunny location. Unheated water is pumped from a storage tank through tubes in the collector, where it absorbs solar heat and is returned to the tank. A second pump moves heated water from the tank through a heating coil. Active solar is compatible with forced air, radiant, or hot water baseboard heat distribution systems.
In an air-based solar heating system, air is heated in a collection point and distributed by a system of fans. The air collection point may be an existing area of the home with good sun exposure and insulated glass, such as a sunroom or sunny living room. Air-based solar is often used to reduce energy consumption by preheating air in conventional HVAC systems.
System setup
An active solar heating system is made up of the solar collector, collector controls, storage system, and distribution system. A hot water heater for domestic water usage can also be incorporated into the system to help offset the system cost and increase efficiency.
Solar collectors may require permits or zoning approval. Also, be sure to research local building codes regarding authorized heating sources, as active solar systems are not approved as primary heating systems in some locations. Even so, they may be a cost-effective way to help reduce energy total consumption.
Solar air collectors may be incorporated into the design of a roof or wall. Most air-based systems are single-room heaters.
Cost
The price tag for an active solar system will vary based on its size and scope. Supplemental and pre-heating solar systems begin at about $3,000, and primary active solar heating systems may go for $15,000. They can pay for themselves in seven to 10 years through energy cost savings. Expect a system lifespan of about 20 years.
Environmental considerations
Solar energy as a home heating source is available free of charge and at no cost to the environment. You can use it to either reduce fossil fuel consumption by supplementing a conventional HVAC system, or eliminate it by pairing it with solar electric power, or other sources of clean energy.

Your best bet
Both geothermal and solar heating can create significant reductions in fossil fuel usage while saving money in the household budget each month. Solar makes a great case for supplemental heating, especially in cold, sunny climates. But the clear winner is geothermal.
Reversible geothermal heat pump technology, using Earth’s thermal mass as a battery and sink, is proven effective and efficient for heating and cooling in the widest range of environments. It can tackle the whole range of HVAC needs for buildings of all sizes, with durable components that will last many decades. And, the higher upfront price is far outweighed by lifetime savings on operational and maintenance costs. If you’re building or renovating a home, and have an extended time horizon to realize the returns, go with geothermal.




